
Calcaneal fractures can also occur with less severe accidents like an ankle sprain or a stress fracture in runners.The talus acting as a wedge causes depression and thus flatten, widen, and shorten the calcaneal body. Predominantly, falls from height and automobile accidents (a foot depressed against an accelerator, brake, or floorboard) are common mechanisms of injury.
Calcaneal fractures are mostly the result of high energy events leading to axial loading of the bone.Mechanism of Injury / Pathological Process Risk factors for calcaneal fractures include: osteoporosis, diabetes mellitus, peripheral neuropathy, osteomalacia, and long-term immunosuppressive therapy.Most patients with calcaneus fractures are young, with the 20-39 age group the most common.20-25% of the cases with a calcaneal fracture is associated with compression fractures of the lumbar vertebrae.

This number increased to 90% for those under 7 years-old. In those 8-14 years-old, 60% of calcaneal fractures are extra-articular.
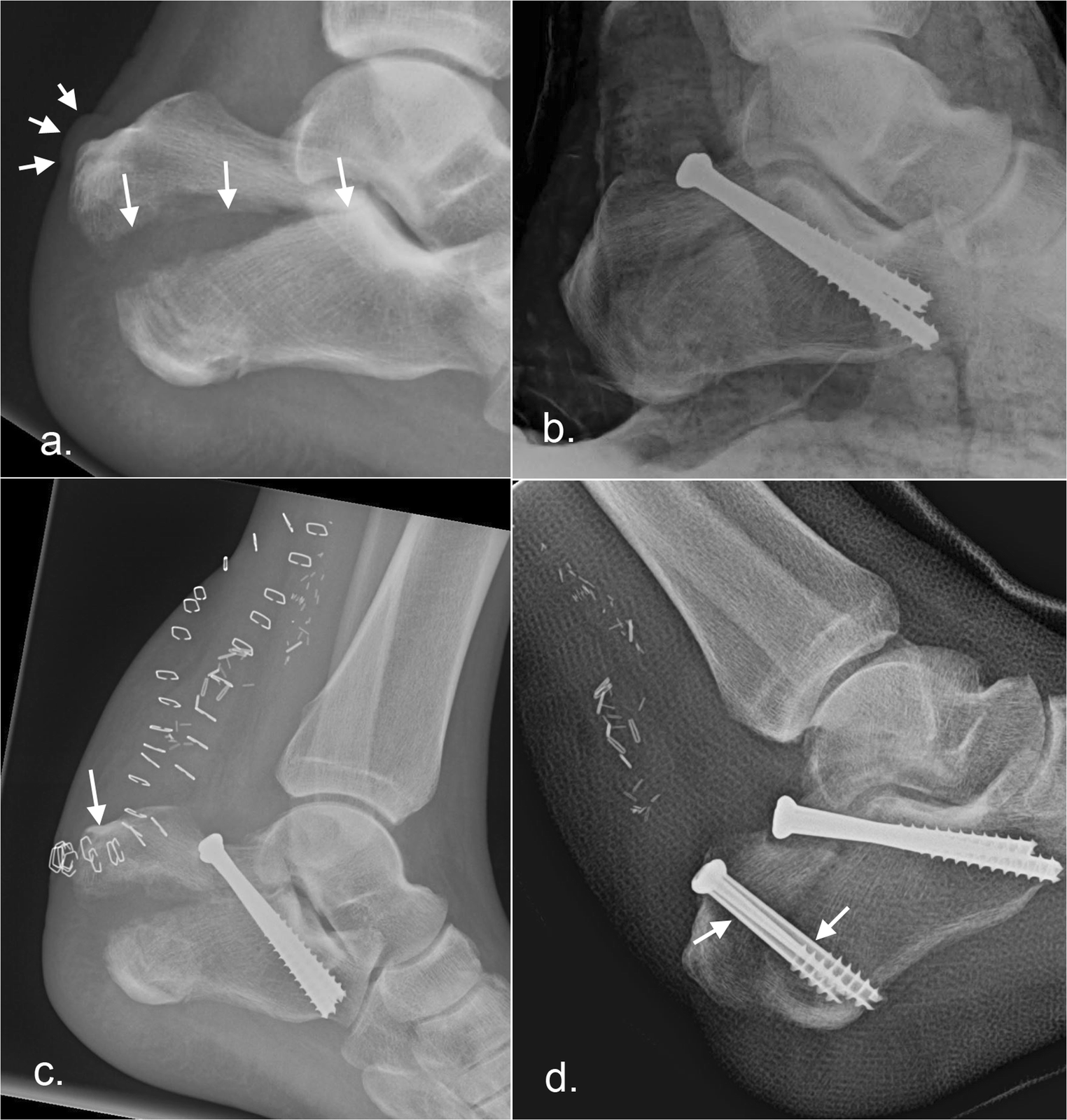
Calcaneal fractures are rare in children. 75% of the calcaneus fracture is intra-articular and the prognosis of intra-articular fracture is poor. But recent studies suggest regional variation in male and female predominance. Earlier, calcaneum fracture was predominately in male as they used to do more industrial work. Less than 10% present as open fractures. Calcaneal fractures account for 1-2% of all fractures and 60% of tarsal fractures. Acts as a lever arm for the gastrocnemius muscle complexĮpidemiology/Etiology. Supports the lateral column of the foot and acts as the main articulation for inversion/eversion. Acts as a foundation and support for the body’s weight. The calcaneus has four important functions: These anatomic landmarks are important because fractures associated with these areas may cause involve joint involvement, tendon and neurovascular injury. The lateral side of the calcaneus and its flat nature is highlighted as the most advantageous for internal fixation, but the poor soft tissue cover challenges wound healing. This also makes surgical approach challenging. The tibial artery, nerve, posterior tibial tendon, and flexor hallucis longus tendon are located medially to the calcaneus and are at risk for impingement with a calcaneal fracture and, as are the peroneal tendons located on the lateral aspect of the calcaneus. The sustentaculum tali is a medial bony projection supporting the neck of the talus. The interosseous ligament and medial, lateral, and posterior talocalcaneal ligaments provide additional support for the joint. Subtalar joint allows inversion and eversion of the foot. It has 4 facets: 1 anteriorly which articulate with cuboid forming calcaneocuboid joint and 3 superiorly (anterior, middle, and posterior, with the posterior facet representing the major weight-bearing surface) which articulate with talus forming talocalcaneal joint (subtalar joint). The calcaneus has a relatively thin cortex. Ĭlinically Relevant Anatomy Ī good understanding of the anatomy of the calcaneus is essential in determining the patterns of injury and treatment goals and options.Ĭalcaneus is the largest talar bone out of 7 tarsal bones which together with the talus form hind-foot. Traditionally, a burst fracture of the calcaneus was known as "Lovers Fracture" as the injury would occur as a suitor would jump off a lover's balcony (axial loading) to avoid detection. It is a rare type of fracture but has potentially debilitating results. /GettyImages-184898128-c2a4bf8d3c7347819b22e69c22a13625.jpg)
Radiological image of calcaneus fracture( lateral view)Ī calcaneus fracture is a heel bone fracture.




/GettyImages-184898128-c2a4bf8d3c7347819b22e69c22a13625.jpg)


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
